Did you know AI can already create amazing music? Yes, that’s right. Not only can this be done in a research context or by coding it yourself, but also on a website where you can simply enter a quick text description of what you want and get a music sample. The best thing is that you can try it for free for up to 20 tries a month. The same team behind Stable Diffusion just released Stable Audio 2.0. Stable Audio by Stability AI works in a very similar way as Stable Diffusion, able to understand the text and transform those abstract words into a musical representation.
How Stable Audio Works
Now, back to generating music with AI. Most new generative approaches, especially involving images and other complex signals, are based on an approach called diffusion networks. For example, Stable Diffusion. But why is this important?

Diffusion models are powerful networks that take noise and can generate an output from it. They do this by learning to add noise repeatedly until it converts back to a real image. This is possible because we train the model in reverse, starting with images and corrupting the image little by little, while also letting the model know how we corrupt it.
Over millions of trials and examples, our model learns the noise pattern and is able to take full noise and construct an output like an image.
The Technical Process Behind Sound Generation
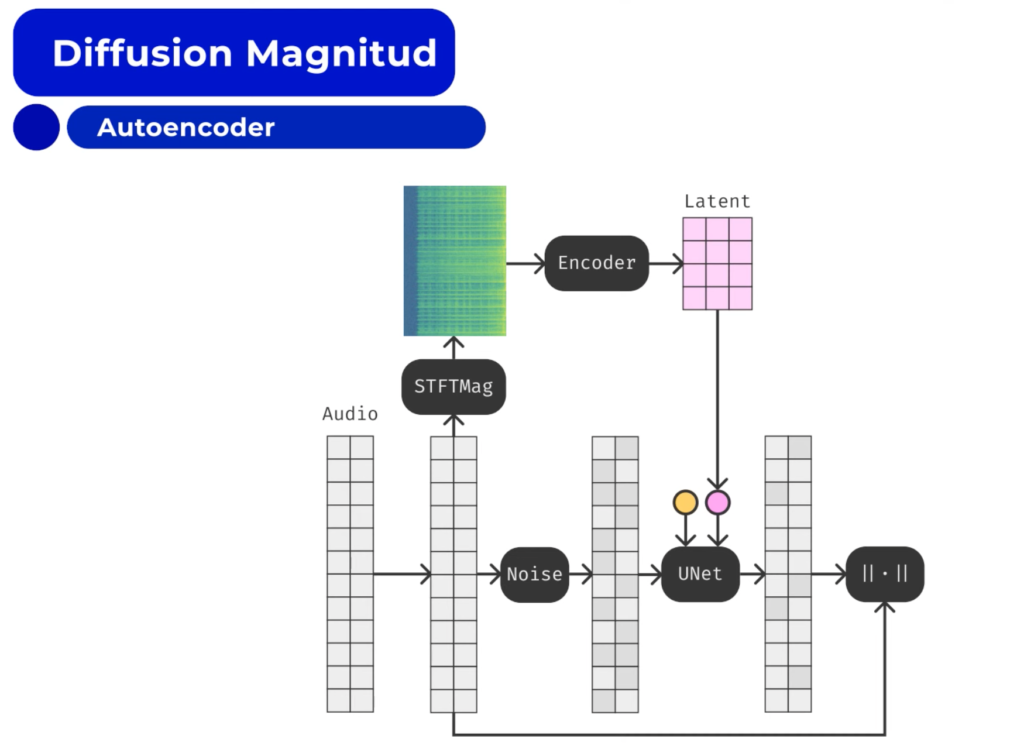
However, we are talking about sound, which is pretty similar to images. A sound can be converted into a magnitude spectrum, which is a visual representation of all the frequency content of the sound over time.

With the x-axis showing time and the y-axis showing frequency, the color also indicates the amplitude of each frequency component. We can use a very similar network to encode the sound into a new representation, which extracts the most important feature of the sound from the original input. This process involves taking our initial audio sample and adding noise to it.
Thanks to the latent information we had previously, we can leverage it to feed information about our initial audio sample and teach our model to reconstruct the sound we fed, which was lost because of the added noise.
The Importance of Variable Output in Music Generation
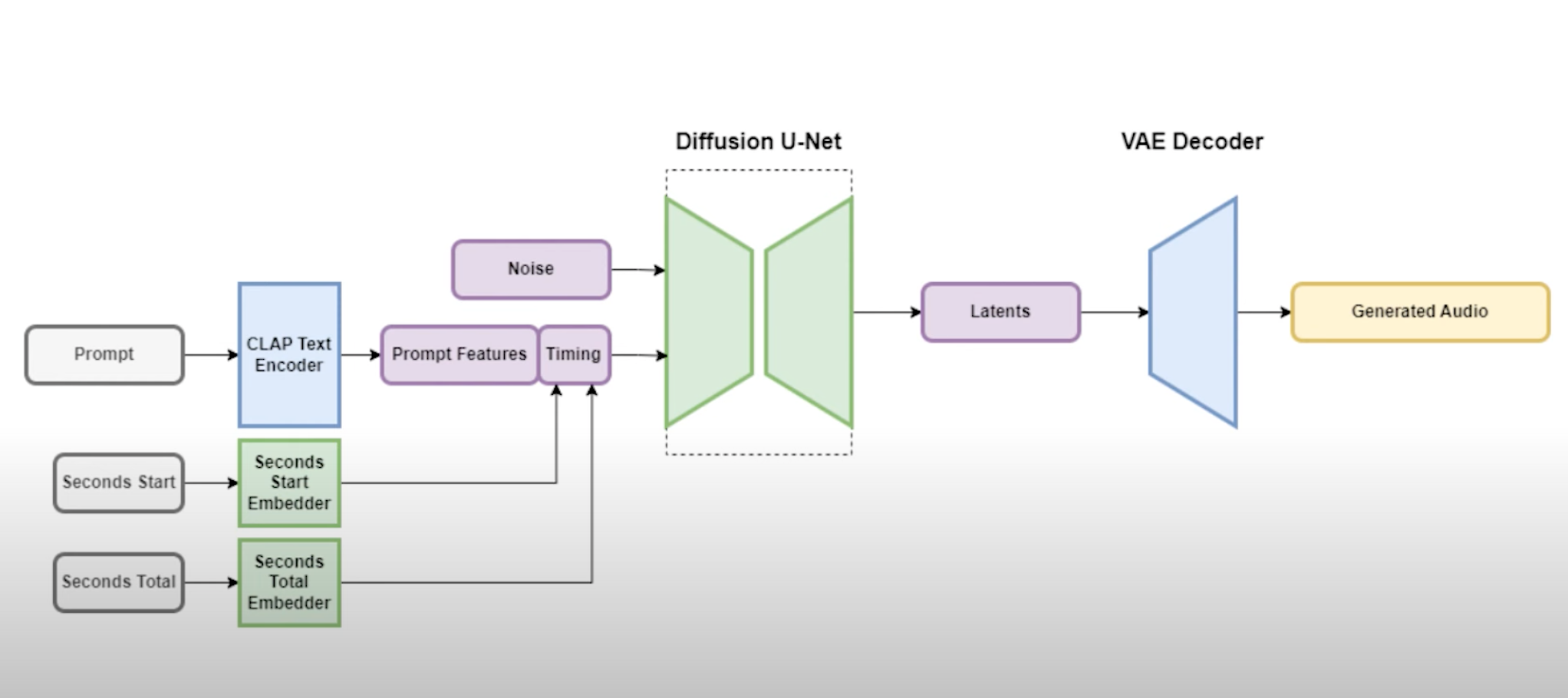
But why is this useful? It allows us to transform pretty much any sort of information into a similar latent representation using different networks trained for that purpose. For example, the CLAP text encoder transforms text input into a good representation for our generative model.
Additionally, they also have a VAE decoder, which works in a compressed representation of sounds for training and inference efficiency. With this model, called Stable Audio, based on the Musa text-to-music generation model, you can quickly generate any song you want following your text input.
Conclusion and Invitations
You can also try the new model on their platform or just listen to the results they shared on their blog post. Please don’t forget to leave a like, subscribe, and let me know what you think of the video and the Stable Audio results. I will see you next time with more exciting new AI research.
Credit: Louis-François Bouchard
Read related articles: